Keys Assignments¶
Assignment 1: Introduction to Your Research¶
Purpose of the Research¶
To create a "Research Object" where anyone can reproduce their research using a living workflow that includes cyberinfrastructure (hardware, orchestration software), containers (specific research software libraries, algorithms, and code), and data.
Previous Research¶
n/a -- this is the bleeding edge!
Describe The Need For The Study¶
Figure credit: Peng 2011 described in the journal Science how reproducible research can be accomplished.
Doing reproducible research is hard!
By providing a templated development environment, using GitHub, GitPod, Docker, and common data science programming languages (R, Python, Java, etc), researchers can use CyVerse to work together more seamlessly and interactively, and students can work asynchronously following easy to follow materials.
Problem Statement¶
How can a researcher or a student get started with these platforms and tools if they've never seen or heard of them them before?
Solution: Develop my own personal profile on GitHub, and add these resources as repositories where others can clone my templates and do their own research.
Helpful Images (Photographs, Tables, Charts, etc)¶
add more here
Assignment 2: Materials and Methods¶
Methods¶
Continuous Integration(CI) requires a platform from which to test software. Continuous Delivery(CD) allows software to be released quickly and reliably. These two continous frameworks are frequently used together as 'CI/CD'.
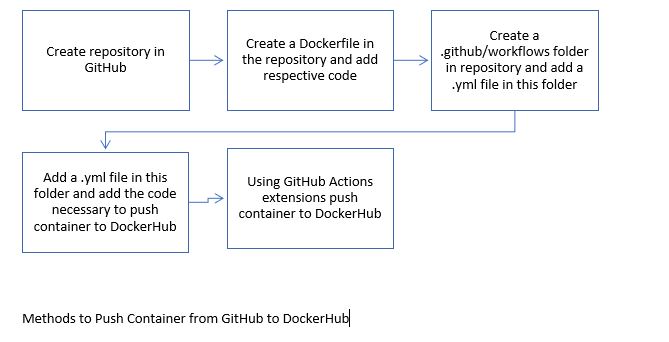
I am using GitHub as the resource for hosting the software CyVerse are working on. GitHub provides "version control" for the code, in case there are any mistakes, they can be reversed. GitHub also supports "Actions" which run software as part of the CI/CD life cycle
I am building software containers with Docker and hosting them on the DockerHub registry. A Docker container has its own operating system, and the specific software I want to run. Docker is an easy way to quickly write code and then run it. When run on the cloud, Docker allows researchers to run whatever they want in the container without having to download the application itself on the host. Containers can be shared so that everyone can have the same copy of the container. Docker can be used to push researchers' applications into a test environment where they can run automated/manual tests. During this research project it will be used to push containers and open them in GitPod and on CyVerse.
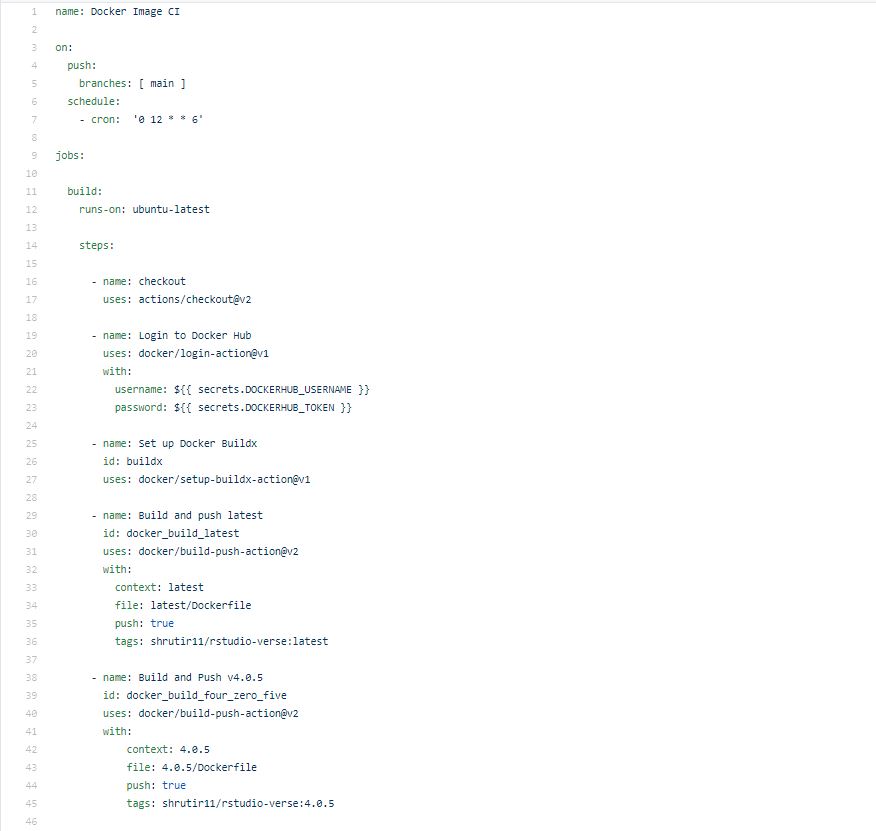
Line 1: This is the name of workflow when the action is running(optional line)
Line 3-5: Establishes the event that triggers the workflow
Line 6-7: The workflow will automatically build and push every Saturday at 12:00 UTC time
Line 9: Groups together all the jobs
Line 11-12: Ensures that the job runs on virtual machine hosted by GitHub
Line 14: Groups together all the steps. The code under this is usually an action or command
Line 16-17:
Materials¶
-
Docker: allows it's users to create containers and run an application such as RStudio Markdown Notebooks or Jupyter Notebooks.
-
DockerHub: a registry of public Docker containers. We will host our public images on DockerHub
-
GitHub Actions: allows for the automation of tasks within your software development life cycle. Through GitHub Actions users can automatically run their software testing scripts. During this intenrship GitHub Actions will be used to push the code from GitHub to DockerHub and open containers such as rstudio-cyverse in Docker.
-
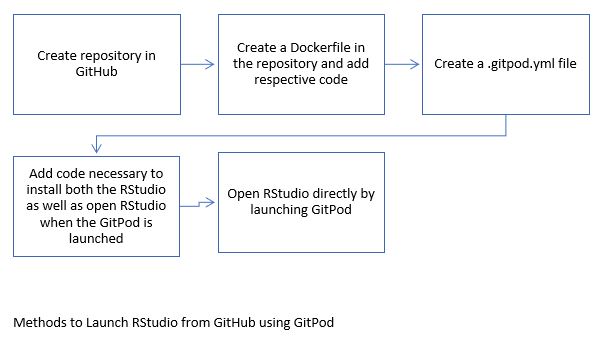
GitPod: GitPod is a fully working environment that can be launched from GitHub. Setting up local dev environments is often very time consuming, but GitPod can do this within a couple of seconds. GitPod includes all the tools and binaries that are available on Linux. During this internship GitPod will be used to help launch RStudio, Jupyter, Java8, and more applications directly from GitHub.
-
Scientific Programming languages: Python, R, Java. Will be used in this internship as an application that will be opened using GitPod from a specific repository.
-
GitHub: Will be used to store repository and code.
Assignment 3: Results¶
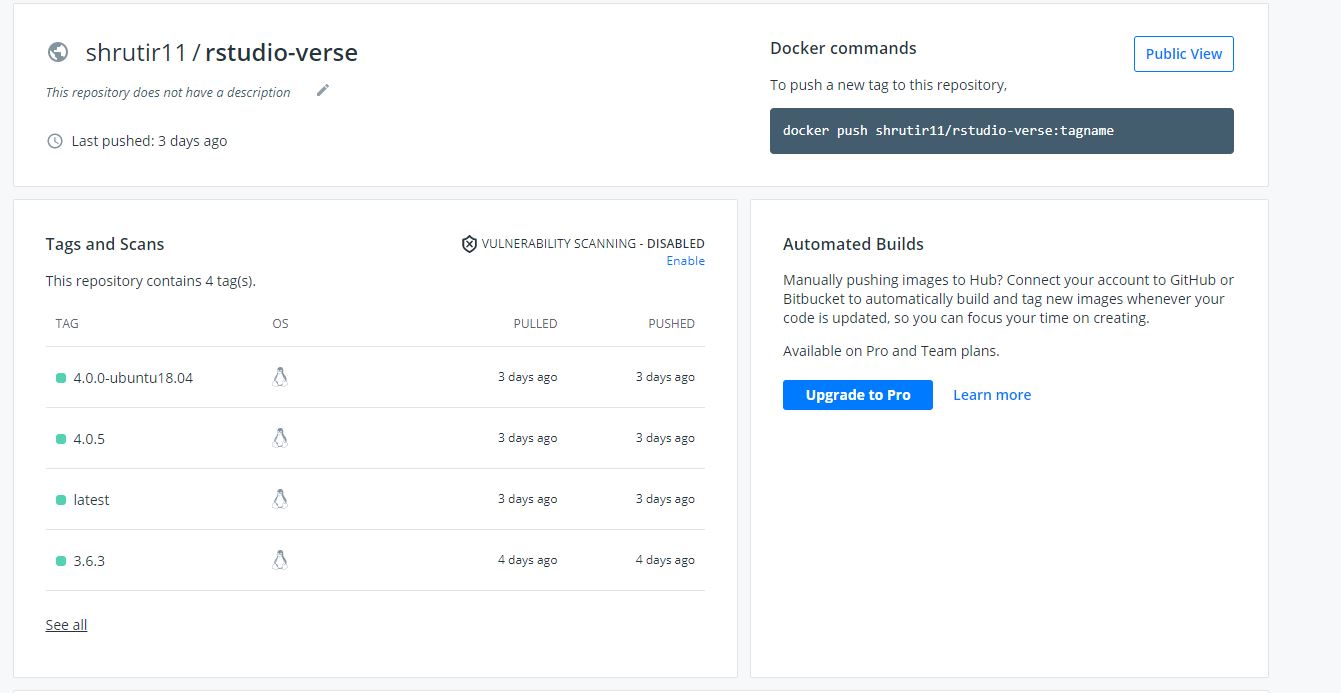
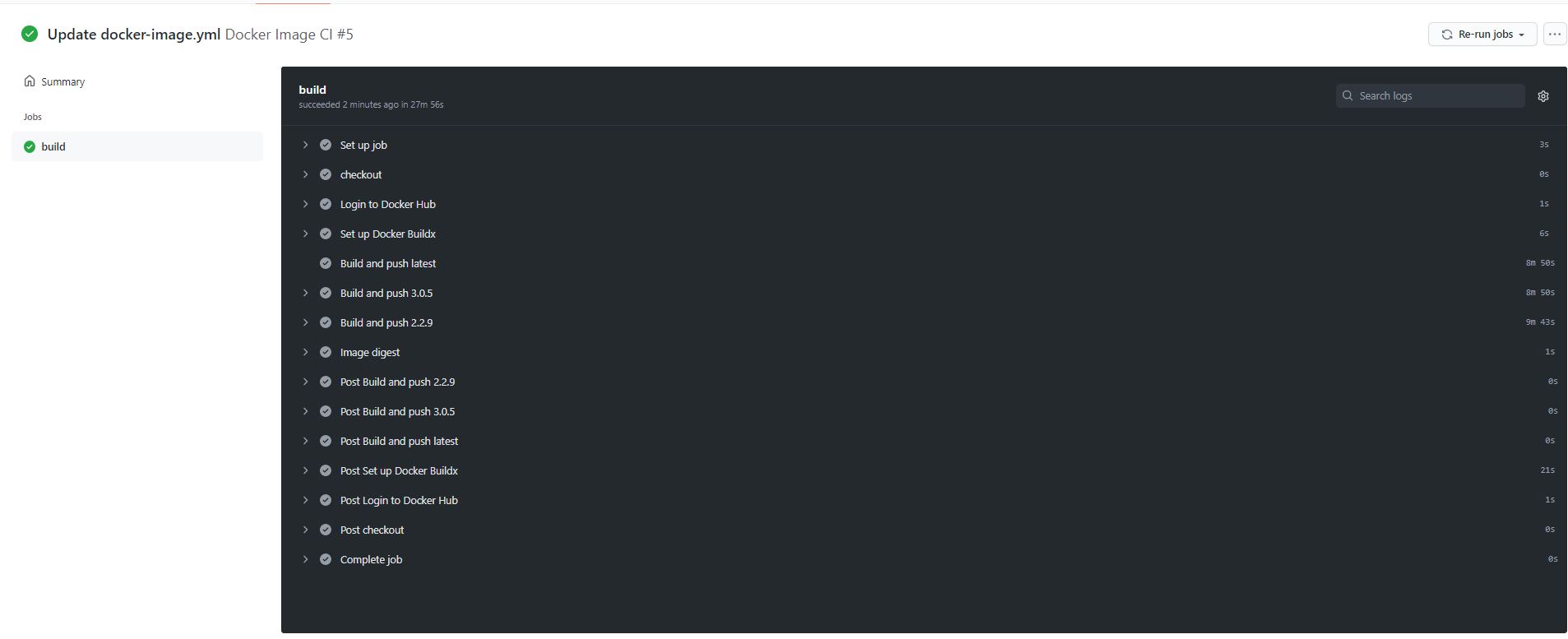
All four versions of RStudio pushed to DockerHub
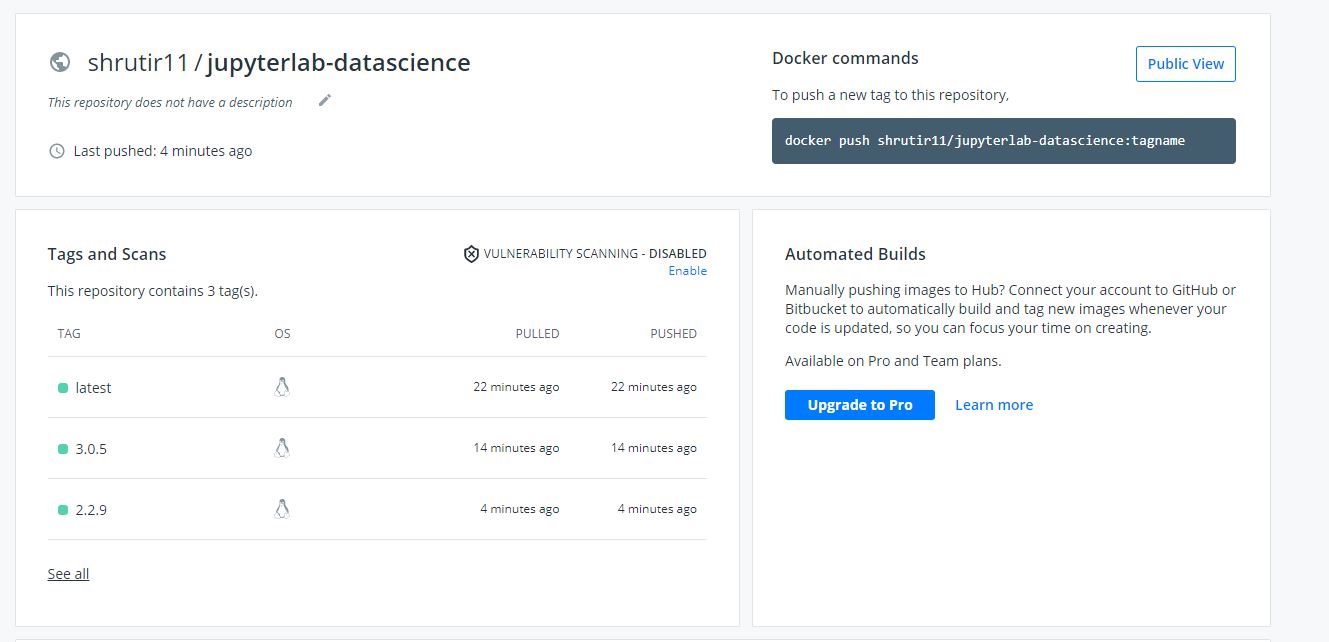
Successful build and push of three versions of JupyterLab using GitHub Actions
All three tagged versions of JupyterLab pushed to Docker using one .yml file
Assignment 4: Conclusion¶
The goal of this project was accomplished. The goal of this project was to create a GitHub account and create repositories within that GitHub account to help scientists do reproducible research online without having much knowledge about platforms such as GitHub, Docker, etc.
To accomplish this goal two different repositories were created. The first repository created pushed a container containing RStudio to DockerHub. I was able to code the .yml file so that four different versions of RStudio were pushed to DockerHub. This was done because some old code can only be viewed on older versions of RStudio while some new code can only be seen on newer versions of DockerHub. The second repository created pushed a container containing three different versions of JuptyerLab to DockerHub for the same reasons stated above.
Scientists who now want to launch containers can click on my profile, clone the repository, and launch the containers. These containers allow scientists to save, track, and share their work thus complying with reproducible science and aiding in the current crisis. It also enable scientists to be able to launch containers without having much knowledge or installing RStudio or JupyterLab on the host.
Assignment 5: Short Abstract¶
As the world shifts to using cloud computing technology its important data scientists begin to adopt techniques which enable reproducible results. The purpose of this project was to create living workflows often called 'continuous integration and continuous development' or CI/CD, using code version control systems, and containerized software. These tools all help data scientists in recording and sharing their research objects. Code repositories were created in GitHub which used continuous 'actions' which pushed pre-compiled software containers to a public container registry (the DockerHub) as well as a private registry. The containers included Linux operating systems and widely used research software languages R and Python as well as their graphic user interfaces (GUI) integrated development environments (IDE): RStudio and JupyterLab, respectively.